215Views 0Comments
The practise of engaging in mental exercises or activities meant to improve cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and problem-solving ability is referred to as brain training. Brain training aims to energise the brain and enhance its general functionality.
There are various ways to train your brain, including with puzzles, games, meditation, and other mental exercises. A number of well-known apps and programmes for brain training make the claim that they may enhance cognitive abilities through a variety of challenging and interactive tasks.
There is conflicting evidence about the efficacy of brain training. Some studies imply that specific types of brain training can enhance cognitive function, while others claim that the advantages are modest and may not transfer to real-world tasks.
However it’s generally agreed that engaging in mentally stimulating activities and pushing oneself to learn and master new skills is good for one’s overall cognitive health.
Who can be benefited from brain training
Brain training can be beneficial for a wide range of individuals, including:
- Older Adults: As we age, our cognitive abilities may decline, and brain training can help to maintain or improve cognitive functioning. Older adults may also benefit from brain training to reduce the risk of cognitive decline and age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s and dementia.
- Students: Brain training can help students improve their memory, attention, and processing speed, which can lead to better academic performance.
- Athletes: Athletes can use brain training to improve their focus, reaction time, and decision-making skills, which can improve their performance in sports.
- Individuals with ADHD: Brain training can help individuals with ADHD improve their ability to focus and pay attention, which can help them better manage their symptoms.
- Individuals with Anxiety or Depression: Brain training can be helpful for individuals with anxiety or depression by providing relaxation techniques and improving cognitive abilities such as attention and problem-solving.
- Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury: Brain training can be helpful for individuals who have experienced a traumatic brain injury by helping them improve cognitive abilities such as memory and attention.

Physiological changes after brain training-
Brain training has been shown to produce a number of physiological changes in the brain. Here are some examples:
- Increased Brain Connectivity: Brain training has been found to increase connectivity between different areas of the brain. This improved connectivity can lead to better cognitive function and overall brain health.
- Enhanced Neuroplasticity: Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to new experiences. Brain training can enhance neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to adapt more quickly and effectively to new situations.
- Improved Blood Flow: Brain training can increase blood flow to the brain, which can improve the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to brain cells, leading to improved cognitive function.
- Reduced Stress: Some brain training techniques, such as meditation, have been shown to reduce stress by lowering levels of the stress hormone cortisol.
- Increased Gray Matter: Gray matter is the part of the brain that contains most of the brain’s nerve cells. Brain training has been found to increase gray matter in certain areas of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in executive functions such as decision-making and planning.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Brain training has been shown to improve cognitive function in a number of areas, including memory, attention, and processing speed.
It’s significant to remember that depending on the type and duration of brain training as well as unique aspects like age and baseline cognitive capability, the magnitude of these physiological changes may differ.

GAMES AND MENTAL EXERCISES THAT CAN BE USED IN BRAIN TRAINING:
There are many games that are often used for brain training, as they require mental effort and can help improve cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Here are a few examples:
- Sudoku: A popular puzzle game that requires logic and problem-solving skills to fill in a grid of numbers.
- Crosswords: Another popular puzzle game that challenges vocabulary and language skills.
- Memory Games: Games that require you to memorize and recall information, such as matching games, word memory games, and memory recall games.
- Strategy Games: Games that require strategic thinking and planning, such as chess, go, and other board games.
- Brain Training Apps: There are many apps available that offer a variety of brain training exercises and games, such as Lumosity, Elevate, and Peak.
- Video Games: Certain types of video games, such as action games and puzzle games, have been shown to improve cognitive abilities such as attention and spatial reasoning.
- Brain Teasers: Brain teasers, such as riddles or logic puzzles, can help improve problem-solving skills and cognitive flexibility.
- Reading: Reading can help improve vocabulary, comprehension, and cognitive function.
- Learning a New Skill: Learning a new skill, such as playing a musical instrument or speaking a new language, can help improve cognitive function and memory.
- Meditation: Meditation can help improve focus and attention and reduce stress and anxiety.
- Visualization Exercises: Visualization exercises, such as visualizing a peaceful scene or a favorite memory, can help reduce stress and improve mood.
- Jigsaw Puzzles: Jigsaw puzzles can help improve spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills.
- Exercise: Exercise can help improve cognitive function by increasing blood flow to the brain and reducing stress.
It’s important to remember that while these games can be beneficial for brain training, they should only be seen as a part of a comprehensive strategy for preserving and enhancing cognitive functioning. Reading, acquiring new skills, and socialising are just a few examples of mentally stimulating activities that might be useful.
Brain training apps
There are many brain training apps available for smartphones and tablets that are designed to improve cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Here are a few examples:

- Lumosity: A popular app that offers a variety of brain training games and exercises to improve cognitive skills.
- Elevate: An app that focuses on improving skills such as memory, focus, and processing speed through a series of daily exercises.
- Peak: An app that offers more than 40 brain training games designed to improve cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- CogniFit Brain Fitness: An app that offers a range of brain training exercises to improve cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and perception.
- BrainHQ: An app that offers a range of exercises and games to improve cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and processing speed.
- Fit Brains Trainer: An app that offers a range of games and exercises to improve cognitive abilities such as memory, focus, and problem-solving.
Devices that are being used for brain trainting
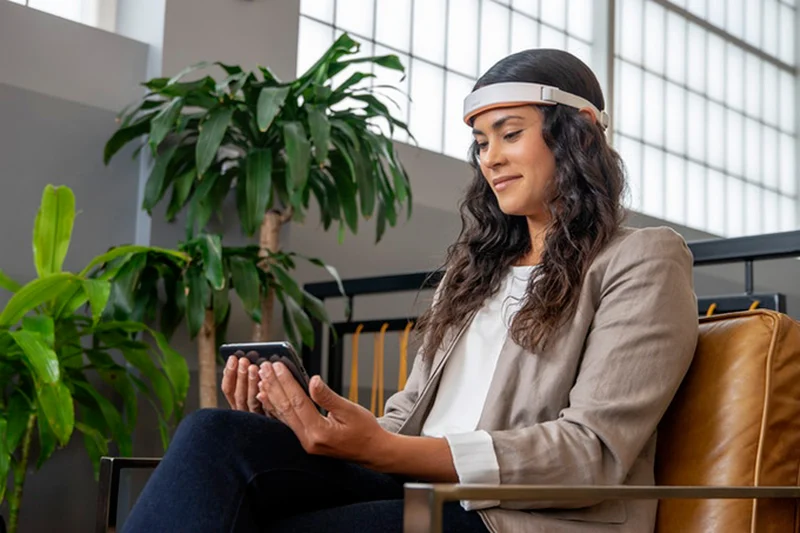

There are several trending devices for brain training that use advanced technology to improve cognitive abilities. Here are a few examples:
- Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets: VR headsets can be used to create immersive environments that challenge cognitive abilities such as spatial reasoning, memory, and attention.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) Headsets: EEG headsets can be used to measure brain activity and provide feedback to help individuals improve their cognitive abilities. These devices are often used in neurofeedback therapy.
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Devices: tDCS devices use electrical currents to stimulate brain activity and improve cognitive abilities. These devices are often used in research studies and clinical trials.
- Neurofeedback Training Devices: Neurofeedback training devices use sensors to measure brain activity and provide feedback to help individuals improve their cognitive abilities. These devices are often used in clinical settings.
- Brain Training Wearables: Wearables such as smartwatches and fitness trackers can be used to track and monitor cognitive abilities such as memory and attention.
- Mendi is a brain training device that uses neurofeedback to improve cognitive abilities such as focus and attention. The device is a headband that contains sensors that measure brain activity and provide real-time feedback to help individuals learn how to control and improve their cognitive functioning. The feedback is presented through a mobile app that provides games and exercises designed to train cognitive abilities such as attention, focus, and relaxation.Mendi uses a type of neurofeedback called passive neurofeedback, which means that it does not require conscious effort from the user. The device measures brain activity and adjusts the feedback accordingly to help the user achieve a state of relaxed focus. This can be helpful for individuals who have difficulty concentrating or who experience stress and anxiety.
- Muse: Muse is a headband that uses EEG technology to provide real-time feedback on brain activity and help individuals improve their cognitive abilities through meditation and relaxation exercises.
- NeuroPlus: NeuroPlus is a brain training platform that uses EEG technology and game-based exercises to improve cognitive abilities such as attention, memory, and impulse control.
- BrainCo FocusFit: BrainCo FocusFit is a brain training headband that uses EEG technology to track brain activity and provide feedback to help individuals improve their cognitive abilities.
- Emotiv Insight: Emotiv Insight is a headset that uses EEG technology to measure brain activity and provide feedback to help individuals improve their cognitive abilities such as focus and attention.
It’s important to keep in mind that while these tools may be beneficial for brain training, they should only be viewed as a part of a comprehensive strategy for preserving and enhancing cognitive performance. Reading, acquiring new skills, and socialising are just a few examples of mentally stimulating activities that might be useful.
TAKEAWAY
Brain training is the practise of performing mental workouts and games to enhance mental acuity and overall brain health. Crossword puzzles, sudoku, memory games, brain teasers, reading, learning a new skill, meditation, visualisation exercises, jigsaw puzzles, and exercise are just a few examples of the many diverse mental activities that can be utilised for brain training. A wide spectrum of people, including older folks, students, athletes, and those with ADHD, anxiety, depression, or traumatic brain injury, can benefit from brain training. Maintaining and enhancing cognitive function requires participating in a variety of mentally engaging activities.